Google Sheets techniques for performance and readability
Contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Why Google Sheets?
- Technique 1: Use Array Formulas
- Technique 2: Use Named Ranges
- Technique 3: Formatting formulas
- Conclusion
Introduction
Google Sheets is a powerful tool that can help with data storage, analysis, and processing. It’s an affordable and accessible tool with a remarkable amount of flexibility. However, as your spreadsheets get more complex, their performance gets noticeably slower and they become more difficult to maintain. In this blog post, we’ll cover some techniques to help you make your Google Sheets faster and easier to maintain.
Why Google Sheets?
Google Sheets is a great choice for small applications where some data needs to be crunched, and the results shown to the user. It’s very accessible, with no cost required on a free Google Account, no need to download and install any local application, and browser based access making it OS-agnostic. Minimal specialised skills are needed by both spreadsheet creators as well as users to leverage the value of Google Spreadsheets. Sharing spreadsheets with people is as simple as granting them permissions and sending them a link.
Technique 1: Use Array Formulas
Using Arrayformulas instead of many individual formulas can help improve both performance and ease of maintenance of spreadsheets.
Arrayformulas can be used by calling the ARRAYFORMULA function and using array ranges instead of individual cell references in the formula.

In many use cases, data will be in a tabular format, with data in a column referencing other data in the same row but in different columns. One common practice is to create the formula for the first row of data, and then copy or drag that formula to every other row in the column. This results in a large number of cells containing formulas, increasing the performance overhead. Maintainability also suffers, with there needing to be checks to ensure that all formulas in a column are appropriately update and aligned.
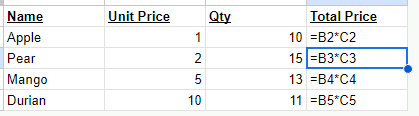
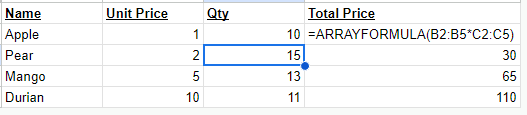
Using array formulas addresses both performance and maintainability concerns. Array formulas incur a noticeably lower performance overhead than columns full of individual formulas. Maintenance is also easier, with only one formula per column needing to be updated and edited.
Template spreadsheets are available to demonstrate the performance difference. The template for individual formulas is here and the one for array formulas is here. Do make your own copies, then try changing the input in the yellow cell and timing how long it takes for the output in the green cell to be updated.

Technique 2: Use Named Ranges
Use Named ranges where possible instead of cell references (eg FRUITS_QTY instead of ‘Fruits Named Ranges’!C2:C5). This makes formulas much easier to read and understand, drastically boosting readability.
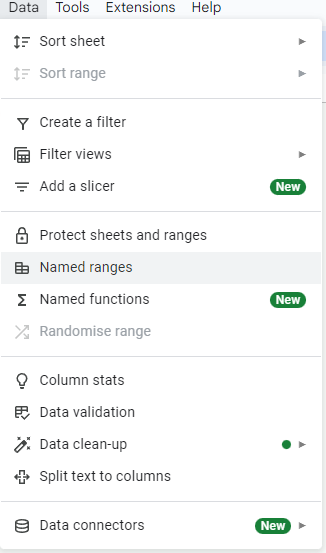
The Named Ranges menu can be accessed by going to Data > Named Ranges, bringing up an interface to input names and ranges that the names should correspond to.
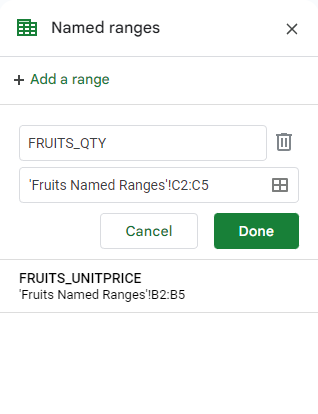
Once created, Named Ranges can be referred to in formulas by their name.

Technique 3: Formatting formulas
Formatting formulas with newlines and indents is another practice that helps to improve the readability and maintainability of spreadsheets.

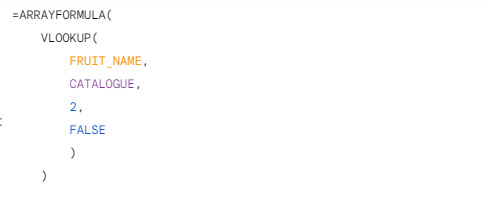
My recommended formatting convention involves having arguments to a formula be one indent to the right of the formula, with each argument on a new line. This makes it easy to quickly identify what the arguments to any given function are, as well as which function an argument is for.
Conclusion
By following these techniques, you can improve the performance of your Google Sheets and make them easier to maintain. Remember to prioritize performance and readability, and use array formulas, named ranges, and formatting. We hope you found these tips helpful and wish you the best of luck in managing your spreadsheets!
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: